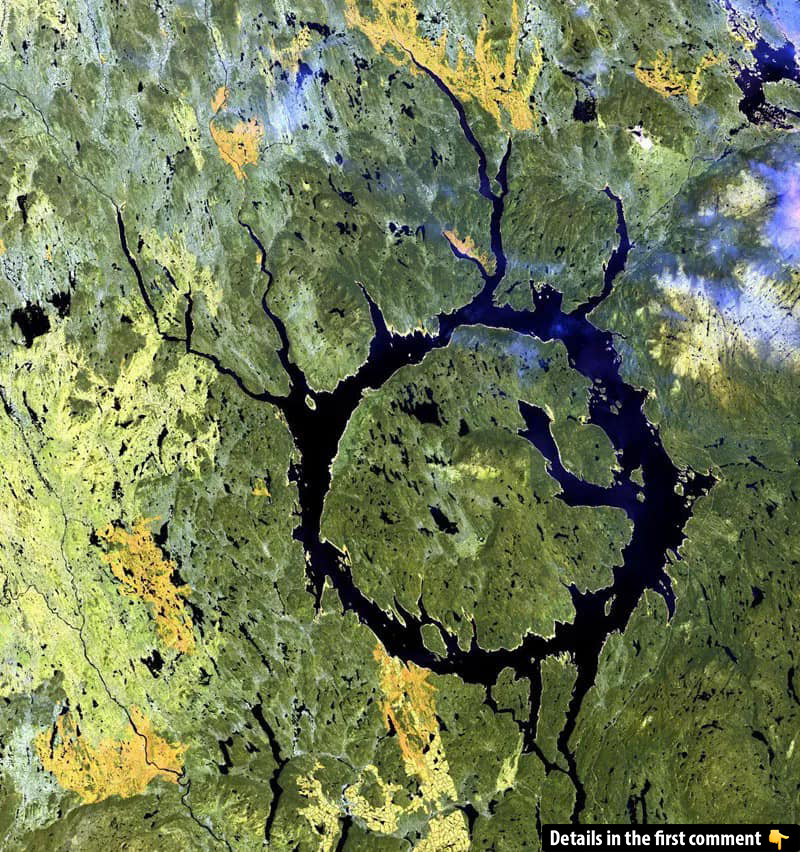
Deep in the heart of Quebec, Canada, lies one of the most fascinating natural features on Earth: the Manicouagan Reservoir. This stunning annular lake, with its shimmering blue waters encircling a prominent island, stands as both a geological marvel and a testament to the power of nature. Known as the “Eye of Quebec” due to its distinct shape visible even from space, the Manicouagan Reservoir has a history that stretches back over 200 million years. It was formed by a colossal meteorite impact that shaped the landscape and left behind a lasting ecological and cultural impact. Today, it serves as an important resource for hydroelectric power generation while also being a captivating subject for scientific research and exploration.
Formation of the Manicouagan Impact Crater
The origins of the Manicouagan Reservoir are nothing short of extraordinary. Around 214 million years ago, during the Late Triassic period, a massive meteorite, estimated to be about five kilometers in diameter, struck the Earth with incredible force. The impact created a vast crater, initially about 100 kilometers wide, although erosion has since reduced its visible diameter to about 72 kilometers. This event formed one of Earth’s most well-preserved impact craters and remains the sixth-largest confirmed impact structure on the planet.
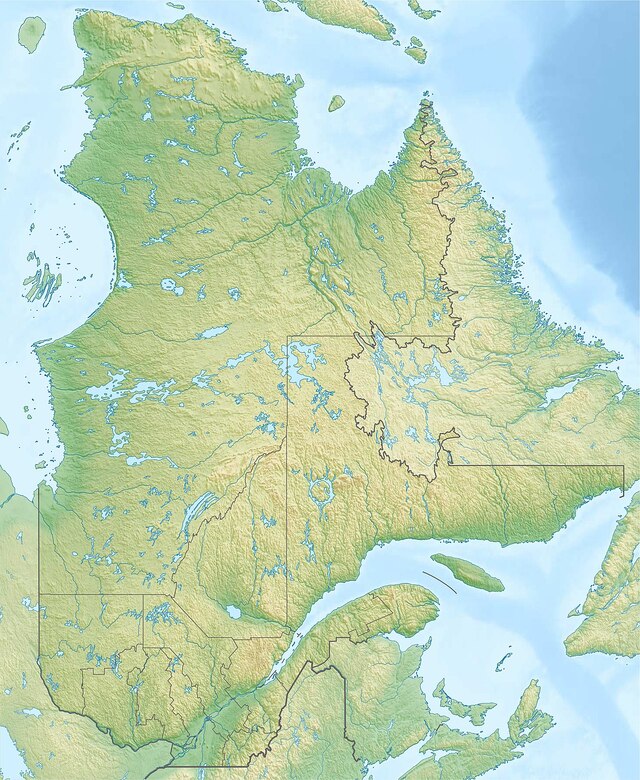
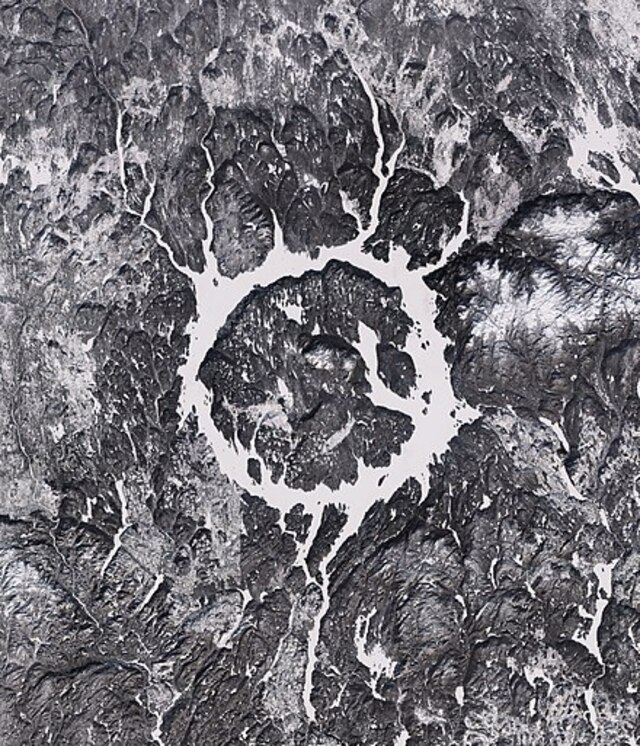
The force of the collision created shockwaves that reverberated across the surrounding region, and the impact caused the target rocks to melt, creating a unique geological record. Over time, glaciation and erosion further shaped the crater, eventually leading to the formation of the striking circular reservoir we see today. At the heart of the crater is René-Levasseur Island, where Mount Babel rises as the highest peak, a remnant of the central uplift that occurred after the impact.
Video
Watch The 100 Kilometer Wide Impact Crater in Canada; Manicouagan Crater to explore this massive geological formation and its history. Don’t miss it!
Geographical Features and Hydrological Importance
Manicouagan Reservoir is not just a remarkable geological structure but also an essential hydrological feature for the region. The reservoir spans an impressive area of 1,942 square kilometers and reaches depths of up to 350 meters. It acts as a crucial headpond for the Manicouagan River, a key waterway that flows through the region. The reservoir feeds several hydroelectric power stations, including the Jean-Lesage generating station and the Daniel-Johnson Dam, which provide electricity to the province of Quebec.
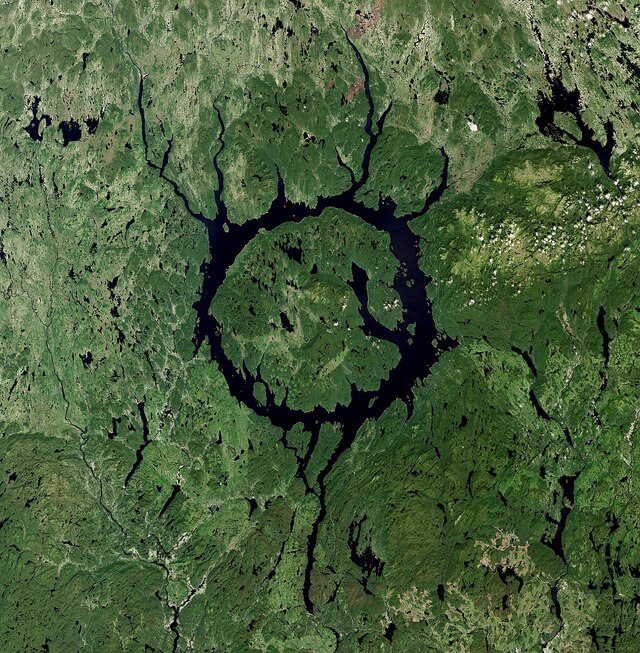

The lake’s annular shape, formed by the remnants of the impact structure, adds to its uniqueness. The surrounding land is rugged, with dense forests and towering mountains, creating a breathtaking landscape. The reservoir is also a key part of the Manicouagan-Outardes hydroelectric project, which has been instrumental in the development of the region’s energy infrastructure. The construction of the Daniel-Johnson Dam in the 1960s transformed the area, flooding the earlier Lake Mushalagan and increasing the size of the reservoir to its present form.
Ecological Features of the Manicouagan Region
Beyond its geological and hydrological significance, the Manicouagan Reservoir and its surrounding areas are home to a diverse ecosystem. The region is rich in wildlife, with dense forests surrounding the lake, providing habitat for a variety of species. The ecological reserves, such as the Louis-Babel Ecological Reserve located on René-Levasseur Island, help protect the unique flora and fauna of the region.
The reservoir itself supports aquatic life, including fish species like the northern pike, lake trout, and yellow perch, which thrive in the cold, clear waters. Birds, such as loons and ducks, are common sights around the lake, adding to the area’s biodiversity. The region’s unique combination of forest, water, and mountains provides an ideal environment for both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
However, the lake’s ecosystem is not without its challenges. The construction of hydroelectric dams, while providing important power for the region, has altered the natural flow of the Manicouagan River and impacted the surrounding habitats. The reservoir’s water levels fluctuate with seasonal changes in energy demand, which can affect local wildlife and plant species that rely on a stable environment. Nonetheless, ongoing conservation efforts continue to protect and maintain the region’s ecological balance.
Human Influence and the Development of the Reservoir
The creation of the Manicouagan Reservoir and its transformation into a major hydroelectric resource had a significant impact on the local communities. The construction of the Daniel-Johnson Dam, which began in the 1960s, flooded the original Lake Mushalagan and reshaped the landscape. The reservoir now serves as a critical source of electricity for Quebec, supporting the energy needs of the province and its inhabitants.
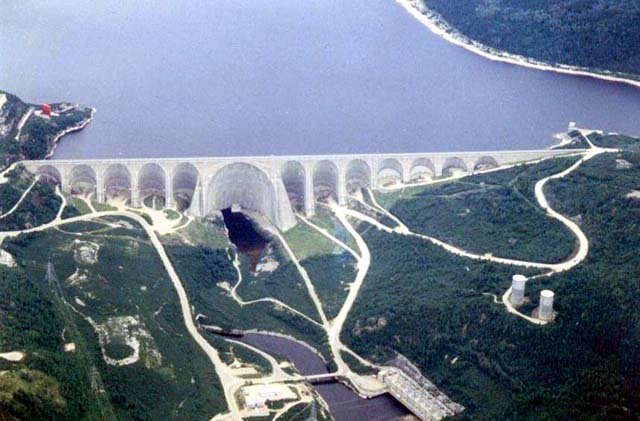

The construction of the dam was part of the larger Manicouagan hydroelectric complex, which was developed by Hydro-Québec, the provincial utility company. The hydroelectric project has been instrumental in Quebec’s growth, providing affordable and renewable energy for homes and businesses throughout the province. Today, the Manicouagan Reservoir continues to play a vital role in the province’s energy production, ensuring that Quebec remains a leader in clean energy generation.
However, the reservoir has also led to changes in local communities, particularly the indigenous groups living in the region. The flooding of areas for hydroelectric development displaced some communities, and the construction of dams and power stations has altered the natural environment in ways that continue to affect local populations. Despite these changes, the region remains a vital part of Quebec’s energy infrastructure and economy.

Cultural and Environmental Impact of the Crater
The Manicouagan Reservoir is not only significant from a scientific and ecological perspective, but it also holds cultural importance for the people of Quebec. The crater, often referred to as the “Eye of Quebec,” is a symbol of the province’s natural beauty and resilience. The impact crater has become a subject of interest for scientists and researchers, who study the area’s geology, hydrology, and ecosystem to better understand Earth’s history and the impact of meteorite collisions.
From a cultural standpoint, the region has become a popular destination for tourists and adventurers seeking to experience its stunning landscapes and unique geological features. The view of the reservoir and the island from space has made it a recognizable symbol of Quebec, often featured in satellite images and environmental studies. The area’s rich natural beauty and historical significance attract visitors from around the world, making it a point of pride for the people of Quebec.
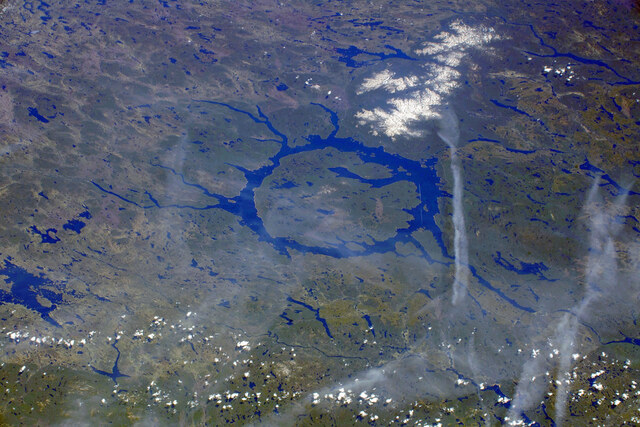

The Manicouagan Crater in Popular Culture and Scientific Research
The Manicouagan impact crater has captured the imagination of not only scientists but also the general public. It is one of the largest and best-preserved impact craters on Earth, offering invaluable insights into the effects of meteorite collisions. Research into the crater has provided important data on the geological processes that shape our planet, including the role of impact events in Earth’s history.
The crater also serves as an educational tool, with studies of the region helping to further our understanding of the environment, natural disasters, and the history of life on Earth. It remains an area of active research, with scientists continuing to explore the impact structure, its effects on the surrounding environment, and its potential link to other significant geological events.
Video
Watch Earth from Space: Manicouagan Crater to see this incredible impact crater from a unique perspective. Don’t miss it!
Conclusion: Preserving and Understanding the Impact of Manicouagan
The Manicouagan Reservoir is a testament to the power of nature and the ingenuity of human development. From its origins as a massive meteorite impact site to its role in powering the province of Quebec, the reservoir has left a lasting legacy on both the environment and the people of the region. While the reservoir’s hydropower production remains a vital part of Quebec’s economy, it is also essential to balance this development with efforts to protect the region’s unique ecology and cultural heritage.
As we continue to explore the mysteries of the Manicouagan crater and its surrounding environment, we gain valuable insights into Earth’s history, the evolution of life, and the resilience of both nature and humanity. The ongoing preservation of the Manicouagan Reservoir ensures that future generations will be able to appreciate its beauty and significance, both as a natural wonder and as a symbol of the enduring power of our planet.



