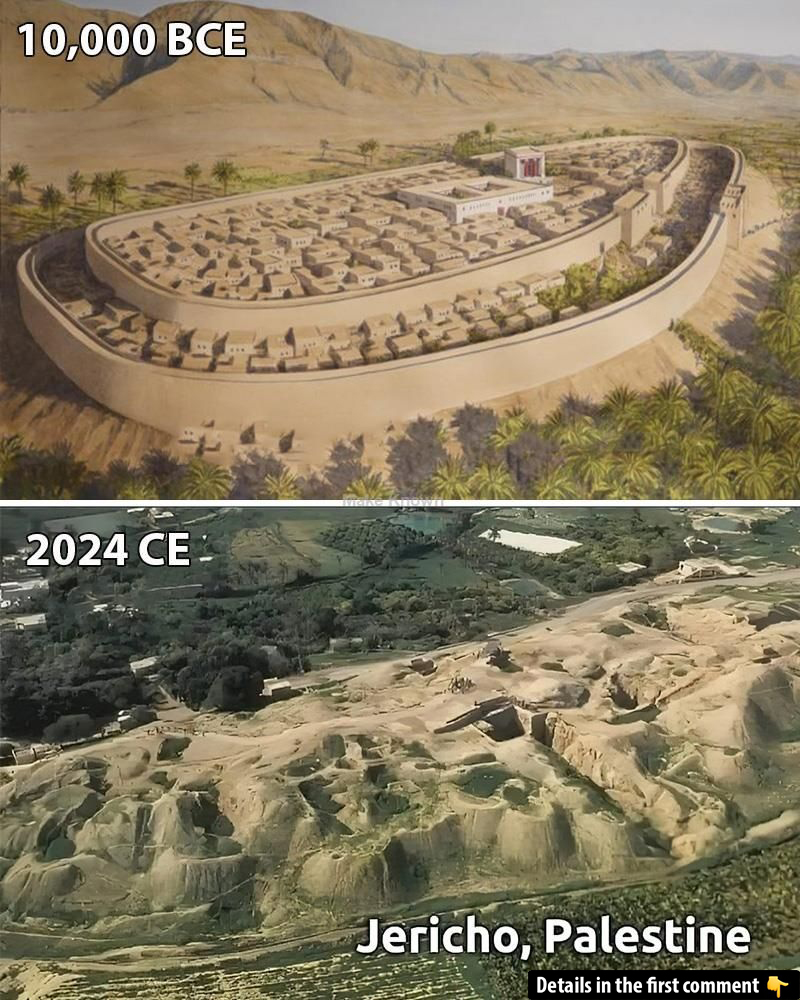
Jericho, one of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities, holds a timeless charm that captivates both historians and travelers alike. Nestled in the fertile Jordan Valley, this ancient city’s rich history stretches back over 10,000 years, offering a unique window into the dawn of human civilization. From its role in biblical tales to its pioneering developments in urbanization and agriculture, Jericho’s story is one of survival, innovation, and resilience. As archaeologists continue to unearth its secrets, Jericho remains a cornerstone of our understanding of the ancient world.
Geographical and Strategic Importance of Jericho
Nestled in the fertile Jordan Valley, Jericho’s location has always been a key element in its survival. The city lies just north of the Dead Sea, and its natural springs, particularly the famous Spring of Elisha, have made it an oasis in the surrounding arid landscape. These springs provided a steady supply of water, making agriculture and settlement possible in an otherwise harsh environment.
Jericho’s position along ancient trade routes further enhanced its significance, making it a crucial point for commerce and interaction between various civilizations in the ancient Near East. Its fertile land and access to trade allowed Jericho to thrive as a center of culture, religion, and commerce for millennia.

Video
Watch the video Jericho – The First City on Earth? in this ancient history documentary.
Historical Timeline of Jericho
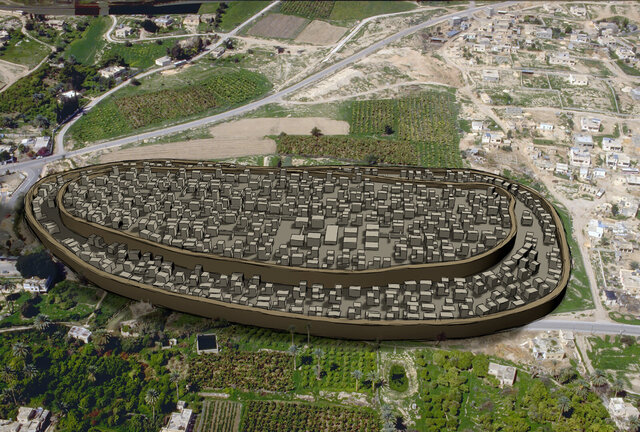
Jericho’s story spans thousands of years, with evidence of human activity dating back to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic period (around 10,000 – 8,000 BC). During this era, Jericho became one of the first permanent settlements in the world. Archaeologists have uncovered monumental structures like the Tower of Jericho, which is believed to be one of the earliest examples of communal architecture. These early inhabitants built substantial stone walls and towers to fortify their settlement, marking the beginning of urbanization in the ancient world.

In the Bronze Age (circa 3,300 – 1,200 BC), Jericho continued to grow, evolving into a fortified city. The famous walls of Jericho, which are mentioned in the biblical story of the Battle of Jericho, were constructed during this period. These walls, built from mud bricks and measuring up to five feet thick, suggest a well-organized society capable of defending itself from external threats. The city’s prosperity continued into the Iron Age (circa 1,200 – 332 BC), during which Jericho saw periods of decline and resurgence under various empires, including the Egyptians, Hittites, and Assyrians.
Religious and Biblical Significance

Jericho’s significance is perhaps most famously tied to its role in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Book of Joshua, the Israelites, led by Joshua, marched around the walled city for seven days. On the seventh day, the priests sounded trumpets, and the walls of Jericho miraculously fell, allowing the Israelites to capture the city. This story has cemented Jericho’s place in religious history and has inspired countless interpretations and studies.

While the biblical account of the fall of Jericho is iconic, its historicity has been debated by scholars and archaeologists. Some argue that the walls described in the Bible may not align with the archaeological evidence, while others see the walls and the destruction of the city as confirming the biblical narrative. Nevertheless, the city’s connection to religious texts continues to attract pilgrims and researchers alike, eager to uncover more about its role in ancient religious history.
Archaeological Discoveries in Jericho
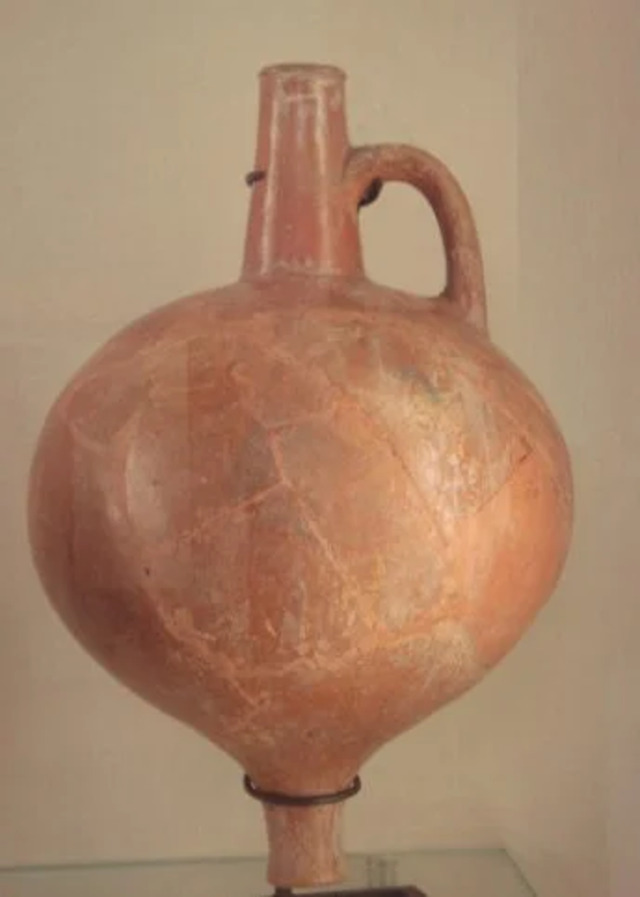

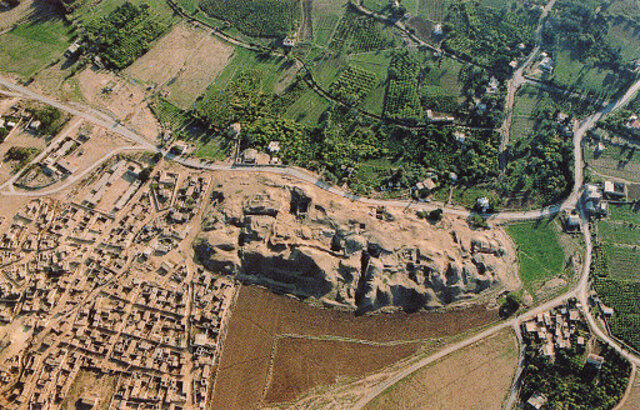
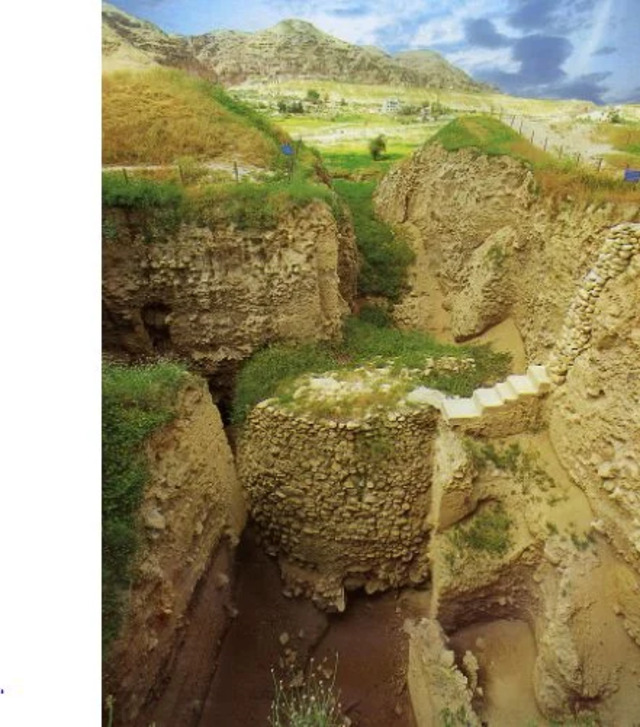
Excavations at Jericho have provided invaluable insights into the city’s past. One of the most significant archaeological discoveries came in the 1950s when Kathleen Kenyon’s team uncovered the remains of a massive wall and a tower, suggesting that Jericho was indeed a fortified city. The wall, dating back to the Early Bronze Age, was found to be at least five feet thick, and the stone tower, nearly eight meters high, was one of the earliest known stone constructions in the world.
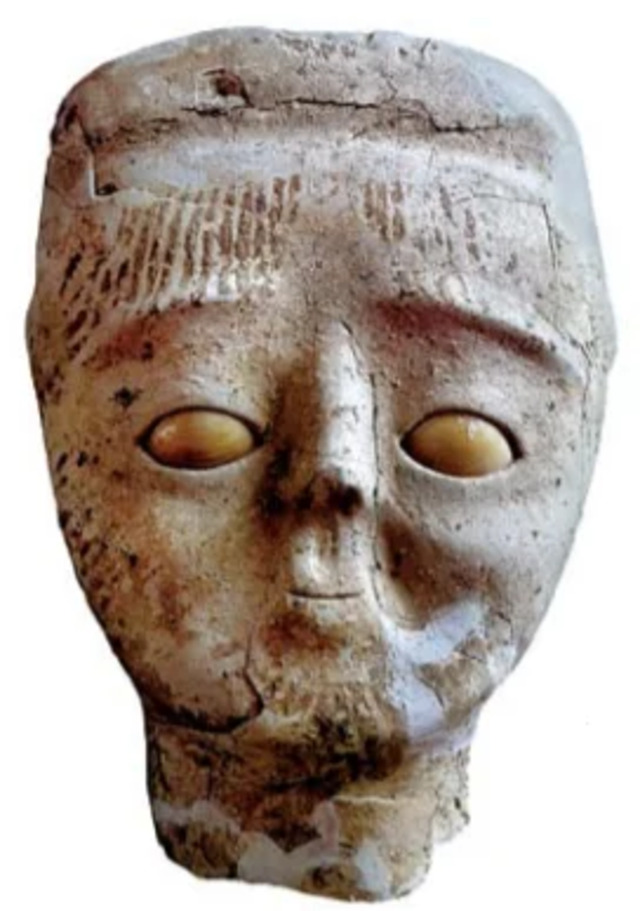

Further excavations revealed a wealth of information about the city’s inhabitants, including burial customs and early agricultural practices. Archaeologists discovered numerous tombs containing plastered skulls, some with facial features recreated in plaster, possibly indicating a form of ancestor worship. The discovery of early agricultural evidence, such as the cultivation of wheat and barley, highlights Jericho’s role in the development of agriculture in the ancient world.
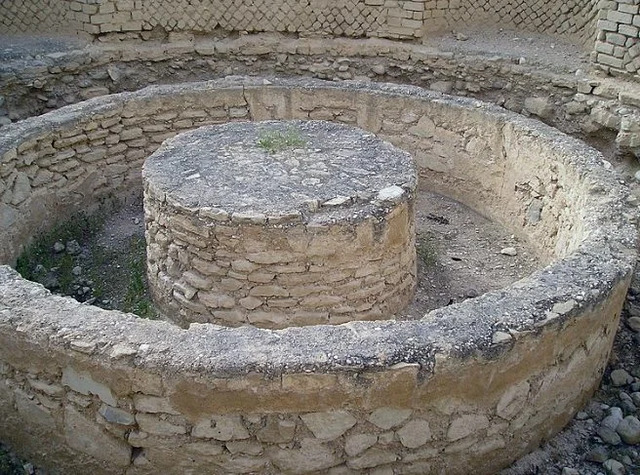

Challenges to Biblical Narratives
While archaeological evidence supports many aspects of Jericho’s history, it has also raised questions about the biblical narrative. The dating of the city’s walls and their destruction has been a subject of debate among scholars. Kathleen Kenyon’s excavations suggested that the walls were destroyed around 1550 BC, which is well before the biblical account of the Israelite conquest. Other archaeologists, such as Bryant Wood, argue for a later date that aligns more closely with the biblical timeline. These differing interpretations highlight the complexity of reconciling archaeological findings with religious texts.
Jericho in the Roman and Byzantine Periods
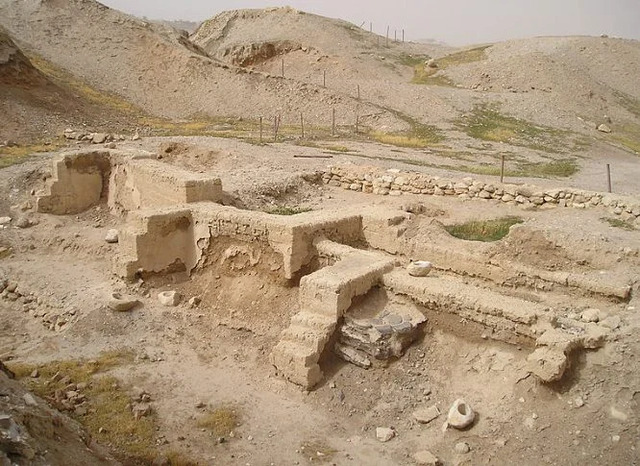

Jericho’s importance continued into the Roman and Byzantine periods. Following its conquest by the Roman general Pompey in 63 BC, Jericho became an important Roman city. Under Roman rule, the city saw significant development, with the construction of palaces, aqueducts, and fortifications. The Romans also established a winter residence in Jericho, and the city became known for its luxurious palaces and gardens.

During the Byzantine period, Jericho continued to be an important cultural and religious center. The construction of churches and monasteries in and around the city reflected the influence of Christianity in the region. Jericho’s strategic location and historical significance made it an important part of the Byzantine Empire’s efforts to control the region.
The Islamic Era to Modern Day Jericho

The Islamic conquest of Jericho in the 7th century AD marked a shift in the city’s significance. Although it lost some of its former prominence, Jericho remained an important settlement during the Mamluk and Ottoman periods. The city became a small village, but its history continued to shape the surrounding region.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, during the British Mandate in Palestine, Jericho began to develop into the modern city that exists today. Despite its challenges, Jericho has retained its rich history and archaeological significance. Today, it is a Palestinian city in the West Bank, known for its historical and religious sites, and continues to be a focal point for research and tourism.
Visiting Jericho Today

For those interested in exploring Jericho’s ancient past, the Tell es-Sultan archaeological site is a must-see. Located just 2.5 kilometers from Jericho’s main square, this ancient settlement mound rises 21 meters above the surrounding area and offers a glimpse into the city’s long history. Visitors can explore the remains of ancient walls, towers, and other structures, providing a tangible connection to the distant past.
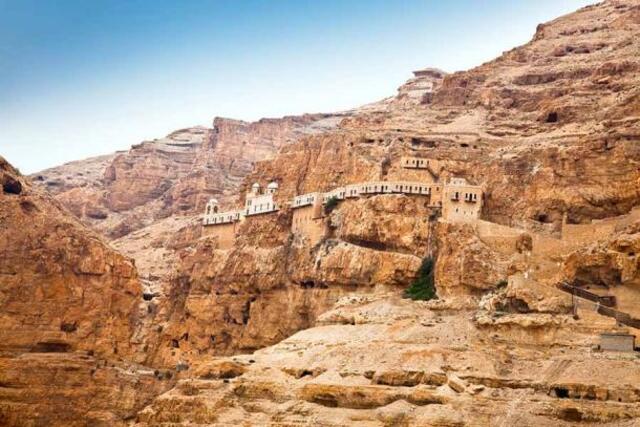

Another significant site in Jericho is the Mount of Temptation, a pilgrimage site where, according to Christian tradition, Jesus fasted after being baptized by John the Baptist. Visitors can either hike up the steep path or take a cable car to reach the summit, where they can enjoy panoramic views of the city and surrounding landscapes.
Video
Watch the video The Walls of Jericho in this Stories of the Bible series.
Conclusion
Jericho’s place in history extends far beyond its biblical connections. As one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, it offers an invaluable window into the development of human civilization. From its early agricultural settlements to its role in religious narratives and its continued existence today, Jericho remains a testament to humanity’s resilience and ingenuity. Whether through its ancient walls, archaeological discoveries, or modern-day significance, Jericho continues to captivate the imagination of those who seek to understand the roots of human history.



