For centuries, the Herculaneum scrolls, buried by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, were thought to be forever unreadable. But now, thanks to groundbreaking advancements in artificial intelligence and particle accelerators, these ancient texts are slowly revealing their secrets. In an extraordinary fusion of technology and archaeology, researchers have uncovered lost words from a scroll that has been locked away for nearly 2,000 years, offering a rare glimpse into the intellectual life of ancient Rome.
Technological Breakthroughs in Decoding the Past
The journey to decipher the Herculaneum scrolls began with a challenge that seemed insurmountable: how to read scrolls that had been burnt to a crisp and carbonized in the intense heat of the eruption. These scrolls, once preserved in the Villa of the Papyri, were thought to be lost forever—too fragile to physically open without crumbling into dust. For centuries, scholars wondered if they would ever be able to access the knowledge contained within them. That is, until scientists, archaeologists, and engineers joined forces to combine advanced imaging techniques and AI tools in a groundbreaking project.

The process starts with the use of synchrotron radiation, a type of particle accelerator that produces extremely powerful X-rays. By shining these high-resolution X-rays onto the scrolls, researchers are able to create 3D scans of the texts without causing any damage. This technology, which is 100 billion times brighter than a hospital X-ray machine, reveals the ink traces that remain hidden inside the fragile papyrus layers.
Next comes the AI component, which helps decipher these hidden texts. The AI, developed through the Vesuvius Challenge, is trained to analyze the X-ray scans and detect faint ink markings. It’s as if the AI is acting as a virtual copyist, recreating the missing words from the scans. The AI’s role is to identify the ink in the images, but human scholars still play a crucial part in piecing together the text and interpreting its meaning.
Video
Check out this video to get the first glimpse inside a burnt scroll that has remained sealed for 2,000 years, uncovered in Italy, offering a rare historical insight.
The Vesuvius Challenge: Collaboration and Innovation
The Vesuvius Challenge, a competition initiated in 2023, was designed to bring together the best minds from around the world to tackle the problem of reading the Herculaneum scrolls. Researchers from various disciplines, including computer science, archaeology, and libraries, came together with the shared goal of deciphering these ancient texts. With the help of machine learning algorithms, the Vesuvius Challenge has led to significant progress in understanding the scrolls, and it continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in archaeological research.

The competition’s ultimate aim is to refine the AI’s ability to identify and decode the ink on the scrolls. While AI has already been able to uncover some text, such as the Greek words “foolish,” “fear,” “disgust,” and “life,” researchers know that there is much more to be discovered. These early successes show promise, but there is still a long way to go before we can fully decipher the entire contents of the scrolls. As Vesuvius Challenge co-founder Brent Seales notes, “This scroll contains more recoverable text than we have ever seen in a scanned Herculaneum scroll.” The advancements in imaging and AI are bringing us closer to unraveling the philosophical thoughts of ancient thinkers.
The Decoding Process: From X-Rays to Ancient Words
So far, the synchrotron scans of scroll PHerc. 172 have revealed some fascinating words. Words like “ἀδιάληπτος” (foolish), “φοβ” (fear), “διατροπή” (disgust), and “βίου” (life) are just a few of the ancient Greek terms that have been uncovered. These words suggest that the scroll could be a work of the philosopher Philodemus of Gadara, whose writings were influential in the development of Epicurean philosophy.

Philodemus, who lived from around 110 to 30 BCE, was known for his philosophical treatises, which explored topics like ethics, happiness, and the nature of pleasure. His writings were widely read in the ancient world and were highly regarded by later thinkers. The discovery of his possible authorship of this scroll opens up new doors for understanding the intellectual climate of the time, providing insight into the ideas that shaped Roman thought.
The AI’s role in this process is pivotal. By scanning the scrolls with the synchrotron and using machine learning to identify ink traces, researchers can recover text that would otherwise be unreadable. As Seales points out, the work done by AI has made it possible to read parts of the scroll that have not been seen for nearly 2,000 years, offering a rare opportunity to connect with the ancient world in a way that was once thought impossible.
Insights into Ancient Greek Texts and the Legacy of Philodemus
The recovery of words like “foolish,” “fear,” “disgust,” and “life” from PHerc. 172 offers a tantalizing glimpse into the intellectual world of ancient Rome. Philodemus was known for his works on ethics and morality, and these newly discovered words may provide clues to his views on human emotions and the nature of existence.
The writing style found on PHerc. 172 closely matches other texts attributed to Philodemus, suggesting that this scroll may be part of his larger body of work. The use of the word “foolish” is particularly notable, as it was a term that appeared frequently in his writings, often in the context of human folly and the pursuit of pleasure. By decoding more of the scroll’s contents, scholars hope to piece together a fuller understanding of Philodemus’s philosophy and its influence on Roman thought.
Moreover, the ability to read these texts could have far-reaching implications for our understanding of ancient Greek and Roman culture. By unlocking the wisdom contained in these scrolls, researchers are not only recovering lost knowledge but also shedding light on the intellectual landscape of the time. The Herculaneum scrolls are a treasure trove of ancient ideas, and their decoding offers a rare opportunity to engage with the past in a meaningful way.
The Historical Significance of the Herculaneum Scrolls
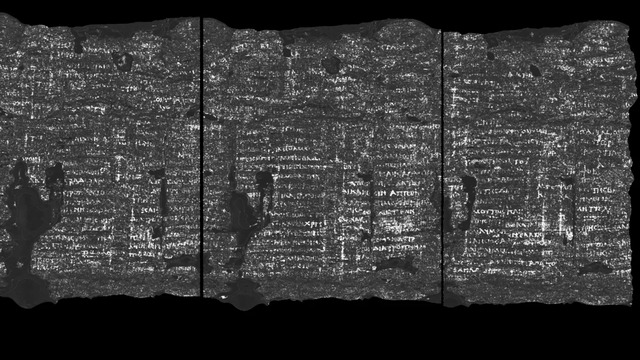
The importance of the Herculaneum scrolls extends beyond their intellectual value. These texts are also crucial for understanding the cultural and historical context of ancient Rome. The scrolls were discovered in the ruins of Herculaneum, a city that, like Pompeii, was destroyed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The volcanic eruption buried the city and preserved many of its buildings, artifacts, and documents, providing a snapshot of life in the Roman Empire at its height.
The Herculaneum scrolls were housed in a villa believed to have belonged to Julius Caesar’s father-in-law. The villa, with its extensive library, offers a unique glimpse into the intellectual life of the Roman elite. The scrolls themselves, though damaged by the heat and carbonization caused by the eruption, have survived as a testament to the resilience of ancient knowledge. With the help of modern technology, we can now begin to unlock the wisdom contained within them, connecting us with the minds of the past in a way that was previously thought impossible.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Future Prospects
While the recovery of text from PHerc. 172 is a major breakthrough, there is still much work to be done. AI technology has made significant strides, but it is not yet perfect. The AI can detect ink, but it still cannot fully recognize the letters or interpret the language in the same way that a human scholar can. This means that experts will continue to play a key role in deciphering the scrolls and piecing together the meaning of the texts.
The Vesuvius Challenge, which encourages researchers to develop better AI tools for analyzing the scrolls, has been instrumental in advancing our ability to read the Herculaneum scrolls. The competition has already led to major breakthroughs, but there is still much more to be done. As technology improves and AI becomes more sophisticated, we may soon be able to read the entire contents of PHerc. 172 and other Herculaneum scrolls, opening up new chapters in our understanding of the ancient world.
Video
Check out this video to learn about the 20-year journey to read the unreadable Herculaneum scrolls, uncovering ancient texts preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius.
Conclusion: Bringing the Ancient World to Light
The successful use of AI and particle accelerators to unlock the secrets of the Herculaneum scrolls marks a momentous achievement in the field of archaeology. For centuries, these ancient texts were thought to be lost forever, but thanks to the collaboration of scientists, archaeologists, and computer experts, we can now begin to recover the knowledge they contain. As more scrolls are decoded, we will gain new insights into the intellectual life of ancient Rome and the minds of its thinkers.
This is just the beginning. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more breakthroughs that will allow us to uncover the mysteries of the past. The Herculaneum scrolls are a testament to the power of collaboration and innovation, and they remind us that the past is never truly lost—sometimes, all it takes is the right combination of technology and determination to bring it back to life.



